Everything You Need To Know About Urine Infection

Urine infections, also known as urinary tract infections (UTIs), are a common health issue that can affect people of all ages. They occur when bacteria enter the urinary tract and multiply, causing discomfort and potential complications. In this blog, we will explore what urine infections are, their symptoms, causes, types, and treatment options. We will also discuss aftercare and prevention tips to help you stay healthy. Also, we will check out why PSRI Hospital is the best urology hospital in India which provides you with the best treatment and care for any urinary health concerns.
What is a Urine Infection?
A urine infection is an infection that occurs in any part of the urinary system, which includes the kidneys, bladder, ureters, and urethra. Most infections involve the lower urinary tract, specifically the bladder and the urethra. When bacteria from the outside enter the urinary tract, they can multiply and cause an infection. This can lead to discomfort, pain, and if left untreated, more serious health issues.
Symptoms of Urine Infection
Recognizing the symptoms of a urine infection early is crucial for timely treatment. Common symptoms include:
- Frequent Urination: A persistent urge to urinate, often producing only small amounts of urine.
- Burning Sensation: A burning feeling when urinating.
- Cloudy Urine: Urine that appears cloudy or has a strong smell.
- Urine Infection in Women: Pink, red, or dark-colored urine indicating the presence of blood.
- Pelvic Pain: Discomfort or pain in the pelvic area, especially in women.
- Lower Abdominal Pain: Pain or pressure in the lower abdomen.
Causes of Urine Infection
Understanding how do you get a urine infection can help in preventing it. Here are some common reasons for urine infections:
Bacterial Entry: The most common cause is bacteria entering the urinary tract through the urethra and multiplying in the bladder.
Incomplete Bladder Emptying: Conditions like an enlarged prostate or certain neurological conditions can prevent the bladder from emptying completely, creating a breeding ground for bacteria.
Sexual Activity: Sexual intercourse can introduce bacteria into the urinary tract, increasing the risk of infection.
Use of Certain Contraceptives: Some types of birth control, like diaphragms, can contribute to bacterial growth.
Urinary Tract Blockages: Kidney stones or an enlarged prostate can block the urinary tract and lead to infections.
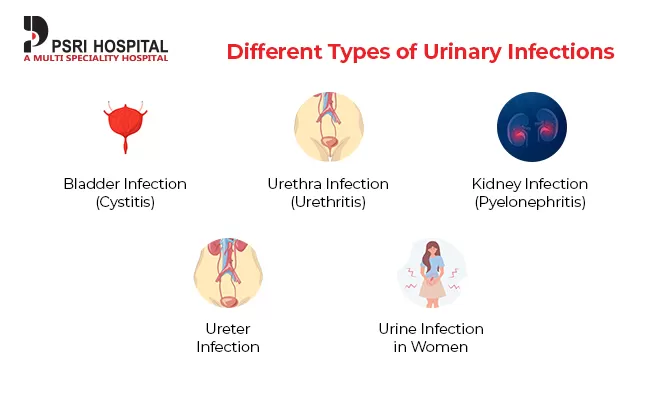
Different Types of Urinary Infections
Urinary infections can occur in different parts of the urinary system, and the type of infection determines the symptoms and treatment approach. The main types are:
Bladder Infection (Cystitis): Bladder infections are the most common type of urinary infection. They occur when bacteria enter the bladder and cause inflammation. Symptoms include frequent urination, burning sensation, and cloudy urine.
Urethra Infection (Urethritis): Urethritis is an infection of the urethra, the tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body. Symptoms include a burning sensation during urination and discharge.
Kidney Infection (Pyelonephritis): A kidney infection is a serious condition that occurs when bacteria spread to the kidneys. Symptoms include fever, chills, back pain, and nausea. It requires immediate medical attention to prevent complications.
Ureter Infection: Infections of the ureters, the tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder, are less common but can occur in conjunction with kidney infections. Symptoms are similar to kidney infections.
Urine Infection in Women: Women are more prone to urine infections than men due to their shorter urethra, which allows bacteria to reach the bladder more easily. Pregnancy, menopause, and certain types of contraception can also increase the risk of urine infection in women.
Treatment Procedures for Urine Infections
Treatment for urine infections depends on the type and severity of the infection. Common treatment options include:
Antibiotics: Antibiotics are the most common treatment for urine infections. They work by killing the bacteria causing the infection. The type and duration of antibiotics depend on the severity of the infection and the patient’s overall health.
Pain Relief: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help manage pain and discomfort during treatment.
Hydration: Drinking plenty of fluids helps flush out bacteria from the urinary tract. Water is the best choice, but cranberry juice is also commonly recommended for its potential benefits in preventing infections.
Hospitalization: Severe infections, especially those affecting the kidneys, may require hospitalization for intravenous antibiotics and fluids.
Aftercare and Prevention
Aftercare is crucial for recovery and preventing future infections. Here are some steps to follow:
Complete Antibiotic Course: Always complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed, even if symptoms improve, to ensure all bacteria are eliminated.
Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to help flush out bacteria and keep your urinary system healthy.
Practice Good Hygiene: Wipe from front to back to prevent bacteria from spreading to the urethra. Urinate after sexual activity to flush out any bacteria that may have entered the urinary tract.
Avoid Irritants: Avoid using feminine hygiene sprays, douches, or powders, which can irritate the urethra and increase the risk of infection.
Regular Check-Ups: Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider can help monitor your urinary health and catch any potential issues early.
How PSRI Hospital Can Help
Urine infections are common but manageable with the right treatment and care. Recognizing the symptoms and seeking prompt medical attention can help prevent complications and ensure faster recovery. PSRI Hospital, recognized as the best urology hospital in India, provides best care for all urinary health concerns. Our best urologist in Delhi NCR is dedicated to providing comprehensive and compassionate care. Contact us today to learn more about our services and how we can help you maintain a healthy urinary system.
FAQs
What causes urine infections?
Ans. Urine infections are typically caused by bacteria entering the urinary tract and multiplying, leading to infection.
How are bladder infections treated?
Ans. Bladder infections are commonly treated with antibiotics, pain relievers, and increased fluid intake.
Why are urine infections more common in women?
Ans. Women have a shorter urethra, which makes it easier for bacteria to reach the bladder and cause an infection.
Can urine infections be prevented?
Ans. Yes, maintaining good hygiene, staying hydrated, and urinating after sexual activity can help prevent urine infections.

 Book An Appointment
Book An Appointment Virtual Consultation
Virtual Consultation





