Understanding Cervical Cancer: A Comprehensive Guide

Cervical cancer is emerging as a significant concern for women worldwide and affecting the well-being of countless individuals, disrupting lives and families. Earlier, it was a sign of concern for middle-aged women. However, times have changed, and women between 35 and 55 are facing this challenge. It is rare in girls under 20, but surprisingly, 20% of cases are found in women older than 65. In this blog, we are going to understand what are the cervical cancer symptoms, causes, and possible treatments for this disease.
What is Cervical Cancer?
Cervical cancer arises in the cells of the cervix – the lower part of the uterus that connects to the vagina. It is not an overnight occurrence but develops over time. Often, it starts as a precancerous condition, but if undetected or untreated, it can turn into a life-threatening disease.
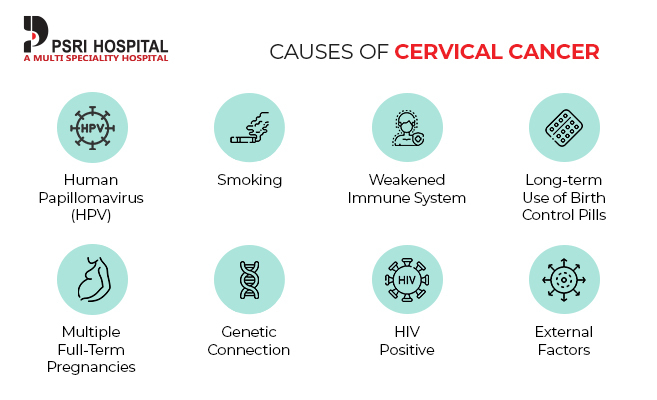
The Causes Behind Cervical Cancer
Understanding the causes of cervical cancer is the first step in prevention and early intervention. There are two kinds: one that is less serious and one that is more likely to turn into cancer. Catching it early can stop it from getting worse with treatments like freezing (cryocautery), burning (electrocautery), or laser therapy. Let’s explore in detail the causes of cervical cancer.
The Role of HPV in Cervical Cancer
One of the most significant cervical cancer reasons is the Human Papillomavirus (HPV). HPV is quite common, and while it often clears on its own without causing any harm, certain types can lead to cervical cancer. These high-risk strains can alter the cervical cells, setting the stage for cancer if not addressed in time. But how does one get HPV? It’s mainly spread through sexual contact. This doesn’t mean that every sexual encounter will lead to HPV or cervical cancer, but it’s important to be aware of the risks. Using protection during sex, limiting the number of sexual partners, and getting vaccinated against HPV can significantly reduce the risk.
Additional Risk Factors
Smoking: The chemicals in cigarettes can damage cervical cells, doubling the risk of cancer.
Weakened Immune System: A compromised immune system is less effective at fighting off HPV infections.
Long-term Use of Birth Control Pills: Using birth control pills for over five years can slightly increase the risk.
Multiple Full-Term Pregnancies: Having many pregnancies or becoming pregnant at a young age can raise the risk, likely due to hormonal changes or immune system impacts.
Genetic Connection: There is a strong family connection to this disease. If your mom or sister has battled it, your own risk doubles. That’s why regular screening tests are so important for those with a family history.
HIV Positive: For those living with HIV, the risk of developing cervical cancer is five times higher. That is why screenings to spot cancer cells early are crucial. Experienced gynecologists usually do these screenings to analyze the size and spread of any tumors. It helps in determining the best course of action, whether it is surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, or targeted therapy for advanced cases.
External Factors: External factors like low socioeconomic status, less education, smoking, and even exposure to DES in the mother’s womb can increase the risk.
Symptoms of Cervical Cancer
Cervical cancer often flies under the radar in its early stages, presenting little to no symptoms. This stealthy nature underscores the importance of regular Pap smears or HPV tests, which can detect changes in cervical cells before they turn into cancer. However, as the disease progresses, certain symptoms can be seen, signaling the need for medical attention. Here are some common cervical cancer symptoms.
Irregular Bleeding as an Early Indicator: Unexpected bleeding, such as bleeding between periods, after sex, or post-menopause, can be a warning sign.
Unusual Discharge and Discomfort: Look out for watery, bloody discharge with a foul odor and pain during intercourse or pelvic pain.
Innovative Treatments at PSRI Hospital
PSRI Hospital is a top cancer hospital in Delhi which understands the fear and uncertainty that a diagnosis of cervical cancer can bring. We offer a range of advanced treatments tailored to each patient’s unique needs. These treatments are:
- Vaccines like Gardasil and Cervarix target the most dangerous strains of HPV (HPV 16 and 18) and are recommended for girls and women from 13 to 45.
- Surgery to remove the cancerous tissues.
- Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays to target cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy is designed to attack cancer throughout the body.
- Targeted therapy for advanced cases.
Our team of specialists works collaboratively to determine the most effective treatment plan, ensuring the highest chances of success.
The Crucial Role of Aftercare
Recovery from cervical cancer doesn’t end with treatment. Aftercare is an integral part of the journey, including regular follow-ups to monitor health, manage side effects, and prevent recurrence. At PSRI Hospital, our commitment extends beyond treatment to include comprehensive aftercare plans. We provide support through rehabilitation, nutritional advice, psychological support, and lifestyle guidance to help our patients reclaim their health and well-being.
Conclusion
Cervical cancer is challenging but not incurable. With early detection, advanced treatments, and comprehensive aftercare, it can be cured. PSRI Hospital is a cancer hospital in delhi ncr which stands as your partner in this journey, offering not just medical treatments but complete care. Our expertise, combined with a deep commitment to our patients’ well-being, makes us the best choice for those seeking care in the face of cervical cancer. Let us be your partner in the fight against cervical cancer, guiding you with knowledge, care, and compassion every step of the way.
FAQs
Can cervical cancer be prevented?
Ans. Yes, cervical cancer can be prevented in many cases. Getting vaccinated against HPV, having regular screenings like Pap smears or HPV tests, using protection during sexual activity, and avoiding smoking can significantly reduce your risk of developing cervical cancer.
How often should I get screened for cervical cancer?
Ans. It depends on your age and health history. Generally, women should start getting Pap smears at age 21 and continue every three years if the results are normal. Starting at age 30, you can get a Pap smear every five years if you also get an HPV test and both results are normal. However, your doctor might suggest a different screening schedule based on your personal health.
What are the treatment options for cervical cancer?
Ans. Treatment options for cervical cancer vary depending on the stage of the cancer and other factors like your overall health and whether you want to have children. Common treatments include surgery to remove the cancer, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or a combination of these methods.
Is cervical cancer curable?
Ans. Yes, cervical cancer is often curable, especially when it is detected early and treated promptly. The success rate of treatment decreases as the cancer progresses, which is why regular screenings and early detection are so important.

 Book An Appointment
Book An Appointment Virtual Consultation
Virtual Consultation





