COPD – Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is more than just a shortness of breath; it is a condition that significantly impacts the lives of millions worldwide. In this comprehensive guide, we aim to shed light on the complexities of COPD, differentiating it from similar respiratory conditions like asthma, and exploring COPD: symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment. Our goal is to offer hope and solutions, showcasing how PSRI Hospital stands at the forefront of pulmonology, critical care & sleep medicine, providing unparalleled care for those in need.
What is COPD?
COPD is a chronic inflammatory lung disease that obstructs airflow from the lungs. It is a term that includes several lung conditions, including emphysema and chronic bronchitis. Unlike some medical conditions that come and go, COPD is a long-term challenge, gradually worsening over time, making every breath a battle.
Asthma vs. COPD
While both asthma and COPD affect the lungs and make breathing difficult, knowing the difference between asthma and COPD is essential. Asthma typically begins in childhood and is characterized by episodes of wheezing and shortness of breath that come and go. COPD, on the other hand, develops due to long-term exposure to lung irritants and is more common in adults over the age of 40. Asthma attacks can be triggered by allergens or physical activity, whereas COPD symptoms are persistent and progressively worsen over time.
Causes of COPD
Here are the causes of COPD:
Primary Causes
Tobacco Smoke: The leading cause of COPD, affecting both smokers and those exposed to secondhand smoke. It damages lung tissue and impairs lung function.
Air Pollution: Pollutants from cars, factories, and even household cleaners can contribute to COPD by irritating the lungs.
Occupational Dust and Chemicals: Long-term exposure to dust in workplaces like construction sites and to chemicals in certain industries can lead to COPD.
Genetics: A condition known as alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency, although less common, can make individuals more susceptible to COPD.
Environmental and Lifestyle Factors
Indoor Air Pollution: From cooking and heating with biomass fuels in poorly ventilated spaces.
Outdoor Air Pollution: Increases the risk of COPD among those living in urban areas with high levels of pollution.
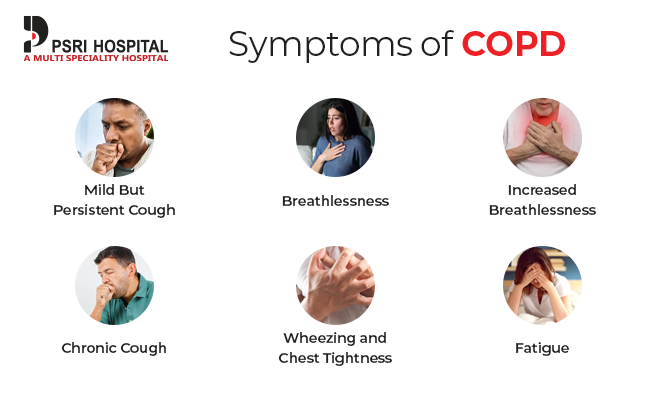
Symptoms of COPD
Symptoms of COPD may start mild and almost unnoticeable but grow more severe over time. They include:
Early Symptoms
Mild But Persistent Cough: Often dismissed as a smoker’s cough or attributed to other causes.
Breathlessness: Initially occurs with exertion but can become a constant issue over time.
Progressive Symptoms
Increased Breathlessness: Even light activities become challenging.
Chronic Cough: Becomes more persistent and severe, often accompanied by mucus.
Wheezing and Chest Tightness: Indicating that airways are narrowing and inflamed.
Advanced Symptoms
Fatigue: A common and debilitating symptom as COPD progresses.
Disturbed Sleep: Resulting from difficulty breathing at night.
Unexpected Weight Loss: Due to increased energy expenditure from the effort to breathe.
COPD Treatment Options
While there is no cure for COPD, treatment can help control symptoms, reduce the risk of complications, and generally improve quality of life. Treatments include:
Medication Management
Bronchodilators: Inhalers that relax muscles around the airways to ease breathing.
Steroids: Inhaled or oral forms reduce inflammation in the airways.
Phosphodiesterase-4 Inhibitors: Specifically for severe COPD to decrease inflammation and relax the airways.
Antibiotics: Used to treat or prevent lung infections, a common complication of COPD.
Pulmonary Rehabilitation
Customized Exercise Programs: Tailored to improve respiratory health without overexertion.
Nutritional Guidance: To support overall lung health and manage COPD symptoms.
Education: On managing symptoms and improving daily life with COPD.
Advanced Treatments
Oxygen Therapy: For those with severe COPD to ensure enough oxygen gets to their organs.
Surgical Options: Including lung volume reduction surgery and, in extreme cases, lung transplants for eligible candidates.
Lifestyle Adjustments
Quitting Smoking: The most impactful change to halt COPD progression.
Avoiding Pollutants: Minimizing exposure to indoor and outdoor pollutants to ease symptoms.
The Aftercare You Need
Managing COPD requires a comprehensive approach that includes:
Follow-Up Visits: Essential to adjust treatments and manage any complications.
Home Monitoring: Keeping track of symptoms and lung function with peak flow meters or spirometers.
Support Groups: Connecting with others living with COPD for shared experiences and advice.
Mental Health Support: Professional counseling to cope with the emotional challenges of living with a chronic condition.
Breathing Exercises: Techniques like pursed-lip breathing to improve lung efficiency.
Staying Active: Maintaining a physically active lifestyle within individual limits to strengthen respiratory muscles.
Balanced Diet: Rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins to support lung health.
Adequate Hydration: Drinking plenty of fluids to keep mucus thin and easier to clear.
Air Quality Improvement: Using air purifiers and maintaining clean indoor environments to reduce irritant exposure.
Conclusion
COPD does not have to be a life sentence of discomfort and limitations. With the right care, support, and treatment, many individuals with COPD can lead fulfilling lives. At PSRI Hospital, we are not just the best cardiac hospital in India; we are leaders in treating chronic conditions like COPD. From understanding the heart transplant cost in Delhi to navigating heart bypass surgery in India, we are here to provide comprehensive care and support. Let us help you breathe easier and embrace life with open arms.

 Book An Appointment
Book An Appointment Virtual Consultation
Virtual Consultation





